Note
Click here to download the full example code
Get the First Syllable of Bout (Bout Duration greater than 1)¶
This example shows how to use the contextual labels to get specific event times
from BirdSongToolbox.import_data import ImportData
import BirdSongToolbox.free_epoch_tools as fet
from BirdSongToolbox.context_hand_labeling import ContextLabels, label_focus_context
from BirdSongToolbox.behave.behave_utils import event_array_maker_chunk, get_events_rasters, repeat_events
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from pathlib import Path
import inspect
Basic Workflow¶
When using BirdSongToolbox you will need to have data in which you want to work on
Although not required, it is convenient to use the Import Classes to import properly formated derived data this way you can guarantee that you have all of the data and meta data needed and that it is all synchronized with each other
As this example assumes that you have not yet configured BirdSongToolbox to automatically know where to look for data we will go through the optional step of telling the toolbox where we would like it to impor from. In this case we will import data used for testing the package. (Don’t worry about this if you are unfamiliar with pytest)
# Select bird_id and session
bird_id = 'z007'
session = 'day-2016-09-09'
src_file_path = inspect.getfile(lambda: None)
project_dir = Path(src_file_path).resolve().parents[1]
print(project_dir)
data_dir = project_dir / "BirdSongToolbox" / "data" / "Chunk_Data_Demo"
# Import Data
zdata = ImportData(bird_id=bird_id, session=session, location=data_dir)
Out:
/Users/darilbrown/PycharmProjects/BirdSongToolbox
Select Male Specific ContextLabel¶
BirdSongToolbox assumes that your behavioral labels are a group of three lists that correspond to the start, end, and label of the vocalizations during a period of time. However, the Chunked Dataformat has multiple tiers of information that include your main subjects behavior, other co-occuring noise, and experimental peridigm metadata. For this reason there is a convenience function for converting the Chunked data behavioral data into the simple list structure.
If you are using behavioral data in a different format you will need to convert them into two lists: - chunk_labels_list - chunk_onsets_list
labels_list: listlist of labels for all epochs for one day
[Chunks] -> [Labels]
onsets_list: listlist of start and end times for all labels for one day
[[Chunks]->[Start Time] , [Chunks]->[End Time]]
Reshape Handlabels into Useful Format
chunk_labels_list, chunk_onsets_list = fet.get_chunk_handlabels(handlabels_list=zdata.song_handlabels)
Contextual Labels of Behavior¶
One of the major uses of BirdSongToolbox is to add additional labels on top of behavioral labels. These additional labels can bee used to contextually sub-select labels based on their identity and context. To do this you must first initiate a ContextLabels instance that is configured to your specific birds behavior. To do this you need three parameters that carry key information about the birds song structure.
Note: In the future I plan to have multiple child class that will be based on the structure of each songbird species structure, but at present the primary class is based on zebra finch song.
These parameters are as follows:
bout_states: dictdictionary of all labels used for specified bird and their context for vocal behavior value for each label can either be ‘not’ or ‘bout’ signifying that it is part of the bout or not
bout_transitions: dictdictionary of the transition label for each state (bout & not) the transition label is indicative of the label that signifies that you have transitioned away from your current state
- Example:
using the configuration used in the code block below
1would be the transition away from the state not being a bout:labels: [8, ‘I’, 8, ‘I’, 1, 7, 1, 3, 7, 4, 8]
state: [‘not’, ‘not’, ‘not’, ‘not’, ‘bout’, ‘bout’, ‘bout’, ‘bout’, ‘bout’, ‘bout’,’not’]
full_bout_length: intLast syllable of the stereotyped portion of the Motif (Not the Intra-Motif note)
# Initialize and configure instance of ContextLabels object
bout_states = {'BUFFER': 'not', 'X': 'not', 8: 'not', 'I': 'not', 'C': 'not', 1: 'bout', 2: 'bout', 3: 'bout',
4: 'bout', 5: 'bout', 6: 'bout', 7: 'bout', 9: 'bout'}
bout_transitions = {'not': 1, 'bout': 8}
full_bout_length = 5
testclass = ContextLabels(bout_states, bout_transitions, full_bout_length)
# Get the Context Array for the Day's Data
test_context = testclass.get_all_context_index_arrays(chunk_labels_list)
Select Behavior using Contextual Information¶
Now that you have contextual labels for your behavioral labels you can begin to sub-select them using boolean operation. The easiest way to do this is to make a one line function and passing it into the label_focus_context helper function in BirdSongToolbox. To do this it helps to know the structure of the basic version of the contextual labels.
contextual_array: array | (labels, 4)Array of context labels for one Epoch(Chunk).
columns: (Motif Sequence in Bout, First Motif (1-hot), Last Motif (1-hot), Last Syllable Dropped (1-hot))
Define Rules for Contextual Selection¶
Now you must define a Function that evaulates labels based on the Context Specified. Walking through the logic of the function below:
Here we are trying to find syllables that occur during the First Motif in the bout, however we only want bouts that have at least two motifs in them.
- This translates to the follow rules:
[1] 1 in the second column (Meaning the syllable occurs during the first Motif of the Bout)
[2] 0 in the third column (Meaning the syllable does not occur during the last motif of the bout).
This ensures that any label selected will be in motif that isn’t both the first and last motif of the bout. However, the syllable will occur during the motif that starts a bout
# Define a context based on the boolean structure of the contextual labels
def first_context_example(order, first, last, ls_drop):
return first == 1 and last == 0
# Select Labels Using Flexible Context Selection
first_syll = label_focus_context(focus=1, labels=chunk_labels_list, starts=chunk_onsets_list[0], contexts=test_context,
context_func=first_context_example)
# Set the Context Windows
first_window = (-500, 800)
# # Clip around Events of Interest
# all_firsts = fet.get_event_related_nd_chunk(chunk_data=proc_data, chunk_indices=first_syll,
# fs=1000, window=first_window )
# all_firsts = fet.event_shape_correction(all_firsts, original_dim=3)
#
# print(np.shape(all_firsts))
first_event_times = fet.make_event_times_axis(first_window, fs=1000)
# Create timeseries representing the labeled Events For all Chunks
event_array_test2 = event_array_maker_chunk(labels_list=chunk_labels_list, onsets_list=chunk_onsets_list)
first_events = get_events_rasters(data=event_array_test2, indices=first_syll, fs=1000, window=first_window)
fill_events_first = repeat_events(first_events)
This will need to wrapped into BirdSongToolbox in a more flexible and modular way
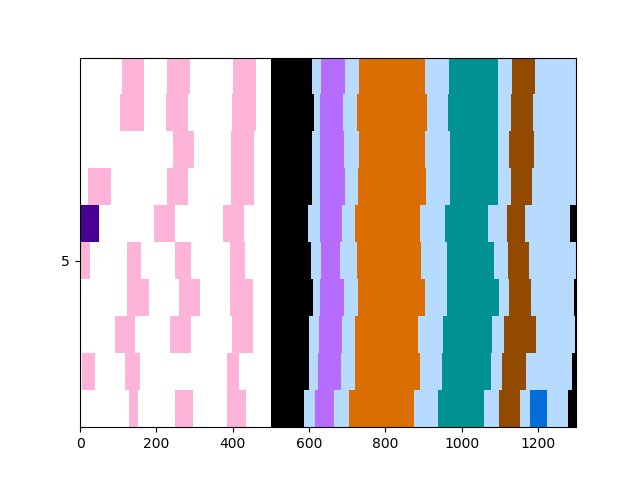
def plot_behavior_test(fill_events_context, context_event_times, context_events, ax=None):
# Setup the Colorbar
cmap2 = matplotlib.colors.ListedColormap(
['#000000', '#B66DFF', '#db6e00', '#009292', '#924900', '#006DDB', '#B6DBFF', 'white', '#feb4d9', '#490092'])
cmap2.set_over('cyan')
cmap2.set_under('#B6DBFF')
bounds = [.5, 1.5, 2.5, 3.5, 4.5, 5.5, 6.5, 7.5, 8.5, 9.5, 10.5]
norm = matplotlib.colors.BoundaryNorm(bounds, cmap2.N)
# PlotBehavior Raster
num_events = context_events.shape[0]
max_len = fill_events_context.shape[0]
bin_width = (max_len) / (num_events)
y_labels = np.arange(0, num_events, 5, dtype=int)
y_steps = np.linspace(0, y_labels[-1] * bin_width, len(y_labels), dtype=int)
y_steps[1:] = y_steps[1:] - int(bin_width / 2)
if ax is None:
plt.imshow(fill_events_context, cmap=cmap2, Norm=norm, aspect="auto")
plt.yticks(ticks=y_steps[1:], labels=y_labels[1:])
plt.ylim(0, max_len)
else:
ax.imshow(fill_events_context, cmap=cmap2, Norm=norm, aspect="auto")
ax.set_yticks(y_steps[1:])
ax.set_yticklabels(y_labels[1:])
ax.set_ylim(0, max_len)
ax.set_xticks([])
# Plot First Behavior Raster
plot_behavior_test(fill_events_context=fill_events_first, context_event_times=first_event_times,
context_events=first_events)
# ax[0].set_title(label="Start of Bout", fontsize=bigsize)
# ax[0].set_ylabel(ylabel='Bout #', fontsize=subsize)
# ax[0].tick_params(axis='both', which='major', labelsize=ticksize)
###############################################################################
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.279 seconds)